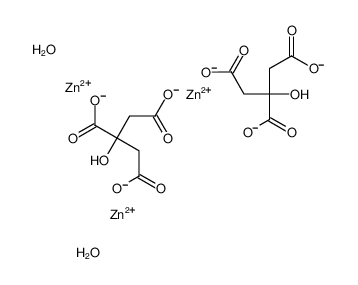
-
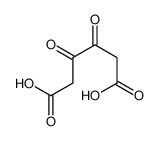
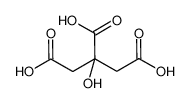
citric acid
CAS No.77-92-9
Formula:C6H8O7
Citric acid is a weak organic tricarboxylic acid having the chemical formula C6H8O7. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the metabolism of all aerobic organisms.
More than a million tons of citric acid are manufactured every year. It is used widely as an acidifier, as a flavoring and chelating agent.
A citrate is a derivative of citric acid; that is, the salts, esters, and the polyatomic anion found in solution. An example of the former, a salt is trisodium citrate; an ester is triethyl citrate. When part of a salt, the formula of the citrate ion is written as C6H5O73− or C3H5O(COO)33−.
3'-hydroxybiphenyl-3-carboxylic acid
1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-
3-hydroxy-3-carboxy-pentanedioic acid
Citric acid
3'-hydroxy-3-biphenylcarboxylic acid
expand collapse
Section 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE/MIXTURE
Product identifiers
Product name : Citric acid
CAS-No. : 77-92-9
Relevant identified uses of the substance or mixture and uses advised against
Identified uses : Laboratory chemicals, Manufacture of substances
Section 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
Classification of the substance or mixture
Classification according to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 [EU-GHS/CLP]
Eye irritation (Category 2)
Classification according to EU Directives 67/548/EEC or 1999/45/EC
Irritating to eyes.
Label elements
Labelling according Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 [CLP]
Pictogram
Signal word Warning
Hazard statement(s)
H319 Causes serious eye irritation.
Precautionary statement(s)
P305 + P351 + P338 IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove
contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing.
Supplemental Hazard none
Statements
According to European Directive 67/548/EEC as amended.
Hazard symbol(s)
R-phrase(s)
R36 Irritating to eyes.
S-phrase(s)
S26 In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and
seek medical advice.
Other hazards - none
Section 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Substances
Formula : C6H8O7
Molecular Weight : 192,12 g/mol
Component Concentration
Citric acid
CAS-No. 77-92-9 -
EC-No. 201-069-1
Section 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
Description of first aid measures
General advice
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
If inhaled
If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. Consult a physician.
In case of skin contact
Wash off with soap and plenty of water. Consult a physician.
In case of eye contact
Rinse thoroughly with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes and consult a physician.
If swallowed
Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water. Consult a physician.
Most important symptoms and effects, both acute and delayed
Vomiting, Diarrhoea, Damage to tooth enamel., Dermatitis, To the best of our knowledge, the chemical,
physical, and toxicological properties have not been thoroughly investigated.
Indication of any immediate medical attention and special treatment needed
no data available
Section 5. FIREFIGHTING MEASURES
Extinguishing media
Suitable extinguishing media
Use water spray, alcohol-resistant foam, dry chemical or carbon dioxide.
Special hazards arising from the substance or mixture
Carbon oxides
Advice for firefighters
Wear self contained breathing apparatus for fire fighting if necessary.
Further information
no data available
Section 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures
Use personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapors, mist or gas. Ensure
adequate ventilation. Avoid breathing dust.
Environmental precautions
Do not let product enter drains.
Methods and materials for containment and cleaning up
Pick up and arrange disposal without creating dust. Sweep up and shovel. Keep in suitable, closed
containers for disposal.
Reference to other sections
For disposal see section 13.
Section 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
Precautions for safe handling
Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols.
Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed.
Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities
Store in cool place. Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place.
Specific end uses
no data available
Section 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS/PERSONAL PROTECTION
Control parameters
Components with workplace control parameters
Exposure controls
Appropriate engineering controls
Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and
at the end of workday.
Personal protective equipment
Eye/face protection
Safety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166 Use equipment for eye protection tested
and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protection
Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique
(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of
contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices.
Wash and dry hands.
The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and
the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Immersion protection
Material: Nitrile rubber
Minimum layer thickness: 0,11 mm
Break through time: > 480 min
Material tested:Dermatril® ( Z677272, Size M)
Splash protection
Material: Nitrile rubber
Minimum layer thickness: 0,11 mm
Break through time: > 30 min
Material tested:Dermatril® ( Z677272, Size M)
data source: KCL GmbH, D-36124 Eichenzell, phone +49 (0)6659 873000, test method: EN374
If used in solution, or mixed with other substances, and under conditions which differ from EN 374,
contact the supplier of the CE approved gloves. This recommendation is advisory only and must
be evaluated by an Industrial Hygienist familiar with the specific situation of anticipated use by our
customers. It should not be construed as offering an approval for any specific use scenario.
Body Protection
impervious clothing, The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the
concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace.
Respiratory protection
For nuisance exposures use type P95 (US) or type P1 (EU EN 143) particle respirator.For higher
level protection use type OV/AG/P99 (US) or type ABEK-P2 (EU EN 143) respirator cartridges.
Use respirators and components tested and approved under appropriate government standards
such as NIOSH (US) or CEN (EU).
Section 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Information on basic physical and chemical properties
a) Appearance Form: crystalline
Colour: white
b) Odour no data available
c) Odour Threshold no data available
d) pH 1,8 at ca.50 g/l at 25 °C
e) Melting point/freezing Melting point/range: 153 - 159 °C - lit.
point
f) Initial boiling point and no data available
boiling range
g) Flash point no data available
h) Evaporation rate no data available
i) Flammability (solid, gas) no data available
j) Upper/lower Lower explosion limit: 8 %(V)
flammability or
explosive limits
k) Vapour pressure no data available
l) Vapour density no data available
m) Relative density no data available
n) Water solubility 383 g/l at 25 °C
o) Partition coefficient: n- log Pow: -1,64 at 20 °C
octanol/water
p) Autoignition no data available
temperature
q) Decomposition no data available
temperature
r) Viscosity no data available
s) Explosive properties no data available
t) Oxidizing properties no data available
Other safety information
no data available
Section 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
Reactivity
no data available
Chemical stability
no data available
Possibility of hazardous reactions
no data available
Conditions to avoid
no data available
Incompatible materials
Oxidizing agents, Bases, Reducing agents, Nitrates
Hazardous decomposition products
Other decomposition products - no data available
Section 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Information on toxicological effects
Acute toxicity
LD50 Oral - rat - 5.400 mg/kg
LD50 Dermal - rat - > 2.000 mg/kg
Skin corrosion/irritation
Skin - rabbit - Mild skin irritation - OECD Test Guideline 404
Serious eye damage/eye irritation
Eyes - rabbit - Irritating to eyes. - OECD Test Guideline 405
Respiratory or skin sensitization
Prolonged or repeated exposure may cause allergic reactions in certain sensitive individuals.
Germ cell mutagenicity
no data available
Carcinogenicity
IARC: No component of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as
probable, possible or confirmed human carcinogen by IARC.
Reproductive toxicity
no data available
Specific target organ toxicity - single exposure
no data available
Specific target organ toxicity - repeated exposure
no data available
Aspiration hazard
no data available
Potential health effects
Inhalation May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation.
Ingestion May be harmful if swallowed.
Skin May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation.
Eyes Causes serious eye irritation.
Signs and Symptoms of Exposure
Vomiting, Diarrhoea, Damage to tooth enamel., Dermatitis, To the best of our knowledge, the chemical,
physical, and toxicological properties have not been thoroughly investigated.
Additional Information
RTECS: GE7350000
Section 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Toxicity
Toxicity to fish mortality LC50 - Leuciscus idus melanotus - 440 mg/l - 48 h
Method: OECD Test Guideline 203
Toxicity to daphnia and static test - Daphnia magna (Water flea) - 1.535 mg/l - 24 h
other aquatic
invertebrates
Persistence and degradability
no data available
Bioaccumulative potential
no data available
Mobility in soil
no data available
Results of PBT and vPvB assessment
no data available
Other adverse effects
no data available
Section 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
Waste treatment methods
Product
Offer surplus and non-recyclable solutions to a licensed disposal company. Dissolve or mix the material
with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber.
Contaminated packaging
Dispose of as unused product.
Section 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
UN number
ADR/RID: - IMDG: - IATA: -
UN proper shipping name
ADR/RID: Not dangerous goods
IMDG: Not dangerous goods
IATA: Not dangerous goods
Transport hazard class(es)
ADR/RID: - IMDG: - IATA: -
Packaging group
ADR/RID: - IMDG: - IATA: -
Environmental hazards
ADR/RID: no IMDG Marine pollutant: no IATA: no
Special precautions for user
no data available
SECTION 15 - REGULATORY INFORMATION
N/A
SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
N/A
1.Synthesis Route
2.Synthesis Route
3.Synthesis Route
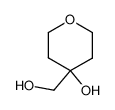
Related Compound Information
Copyright © 2015 MOLBASE All Rights Reserved.
ICP Shanghai 14014220





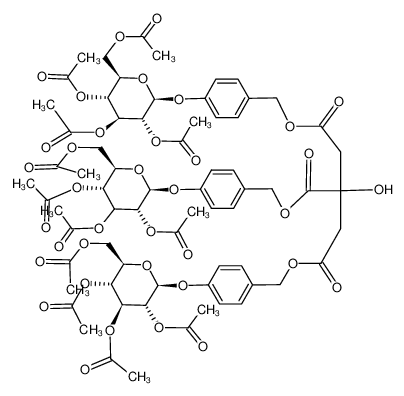

![952283-93-1 spectrum, 2-[4-O-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)benzyl] citrate](http://saasimg.molbase.net/mol_command/1a311c90adf94aba94936bcd19ca6ba3.png)